Luxembourg ID
Introduction
Interface Summary
export interface AbstractEidLux {
allData(filters: string[] | Options, callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenAllDataResponse) => void): Promise<TokenAllDataResponse>;
allCerts(parseCerts?: boolean, filters?: string[] | Options, callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenAllCertsResponse) => void): Promise<TokenAllCertsResponse>;
biometric(callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenBiometricDataResponse) => void): Promise<TokenBiometricDataResponse>;
tokenData(callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenInfoResponse) => void): Promise<TokenInfoResponse>;
address(callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenAddressResponse) => void): Promise<TokenAddressResponse>;
picture(callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenPictureResponse) => void): Promise<TokenPictureResponse>;
rootCertificate(parseCerts?: boolean, callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenCertificateResponse) => void): Promise<TokenCertificateResponse>;
authenticationCertificate(parseCerts?: boolean, callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenCertificateResponse) => void): Promise<TokenCertificateResponse>;
nonRepudiationCertificate(parseCerts?: boolean, callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenCertificateResponse) => void): Promise<TokenCertificateResponse>;
allCertsExtended(parseCerts?: boolean, filters?: string[] | Options, callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenAllCertsExtendedResponse) => void): Promise<TokenAllCertsExtendedResponse>;
rootCertificateExtended(parseCerts?: boolean, callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenCertificateExtendedResponse) => void): Promise<TokenCertificateExtendedResponse>;
authenticationCertificateExtended(parseCerts?: boolean, callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenCertificateExtendedResponse) => void): Promise<TokenCertificateExtendedResponse>;
nonRepudiationCertificateExtended(parseCerts?: boolean, callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenCertificateExtendedResponse) => void): Promise<TokenCertificateExtendedResponse>;
verifyPin(body: TokenVerifyPinData, callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenVerifyPinResponse) => void): Promise<TokenVerifyPinResponse>;
authenticate(body: TokenAuthenticateOrSignData, callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenAuthenticateResponse) => void): Promise<TokenAuthenticateResponse>;
sign(body: TokenAuthenticateOrSignData, bulk?: boolean, callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenSignResponse) => void): Promise<TokenSignResponse>;
signRaw(body: TokenAuthenticateOrSignData, bulk?: boolean, callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenSignResponse) => void): Promise<TokenSignResponse>;
allAlgoRefs(callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: TokenAlgorithmReferencesResponse) => void): Promise<TokenAlgorithmReferencesResponse>
resetBulkPin(callback?: (error: T1CLibException, data: BoolDataResponse) => void): Promise<BoolDataResponse>;}
export class PinType {
static PIN = 'Pin';
static CAN = 'Can';
}
Get Luxembourg ID container object
Obtain the Reader-ID
Cardholder Information
Biometric Information
Address
Picture
Signature Image
Certificates
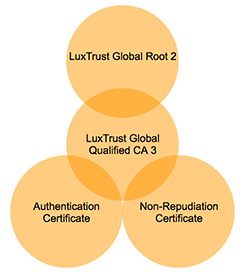
Certificate Chain
Extended certificates
Root Certificate
Authentication Certificate
Non-repudiation Certificate
Data Filter
Filter Card Holder Information
Filter Certificates
Sign Data
Sign Hash
Calculate Hash
Raw data signing
Verify PIN
Verify PIN without pin-pad
Verify PIN - retries left
Authentication
Error Handling
Error Object
Was this helpful?
